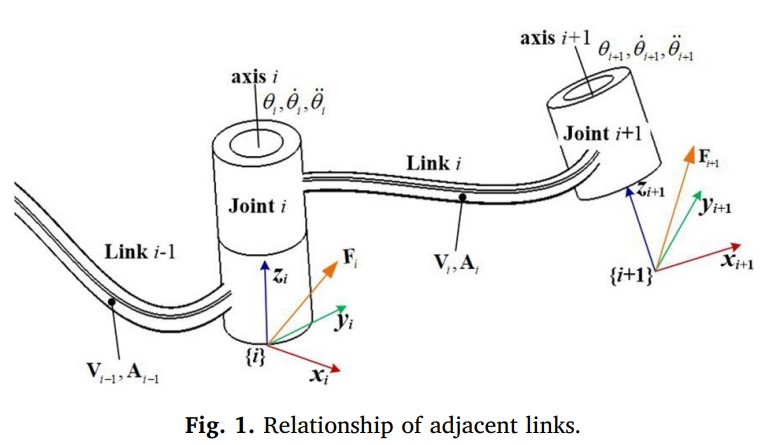
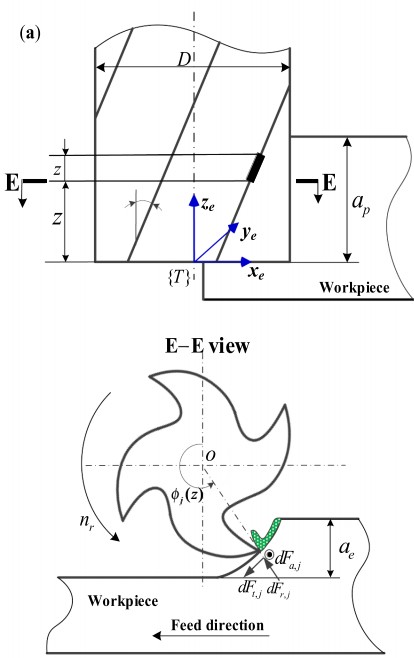
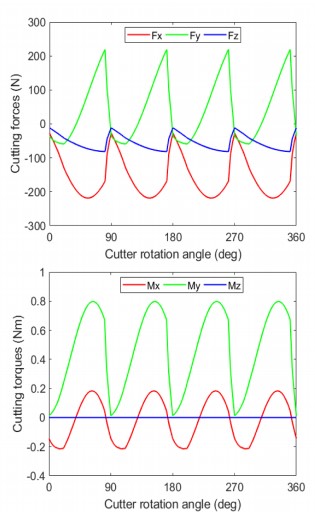
在机器人加工过程中,由于外部刀-工件相互作用引起的串联结构的运动学误差和柔顺性误差会导致期望轨迹产生相当大的偏差。因此,本文基于李理论建立了运动学误差和柔度误差的统一误差模型,提出了一种高效的串联加工机器人运动学参数和关节柔度的标定方法。该方法通过对运动学误差模型的分析,研究运动学误差的传播规律,从而得到相应的等效运动学误差模型,其中将关节偏移误差视为扭转(关节扭转和参考构型扭转)误差的一个来源。在此基础上,对连杆自重和切削载荷引起的关节柔顺误差进行分段建模,通过机器人末端切割器构型误差的线性叠加,分别由运动学误差和柔顺误差计算得到统一的误差模型。最终得到标定后的运动学参数和关节柔顺度,并用于补偿串联加工机器人的运动学和柔顺度误差。最后,为了验证所提出的统一误差模型的有效性,采用6自由度串联加工机器人KUKAKR500进行仿真分析。标定参数之间的比较表明,统一误差模型具有最优标定构型,计算效率更高,适用于实际加工应用中运动学参数和关节柔度的标定。
Cuttergeometry
Cutting payloadscalculation
该文章信息如下:
标题:Analysis of unified error model and simulated parameters calibration for robotic machining based on Lie theory
作者:Zhongtao Fua,Jian S Dai,Kun Yang,Xubing Chen,Pablo López-Custodio
摘要:In robotic machining process, the kinematic errors of serial structure and compliance errors caused by external cutter-workpiece interactions can result in considerable deviation of the desired trajectory. Therefore, this paper proposes an efficient calibration methodology by establishing a unified error model about kinematic errors and compliance errors based on Lie theory, which simultaneously calibrates the kinematic parameters and joint compliances of a serial machining robot. In this methodology, the propagation law of kinematic errors is investigated by analysis of the kinematic error model, and the corresponding equivalent kinematic error model is thus obtained, in which the joint offset errors are regarded as one source of twist (joint twist and reference configuration twist) errors. On this basis, with the segmentation and modelling of the joint compliance errors caused by the link self-weight and cutting payloads, the unified error model is developed by linear superposition of configuration errors of the robotic end-cutter, calculated from the kinematic errors and compliance errors respectively. Meanwhile, to improve the accuracy of parameters calibration, the observability index is adopted to optimize the calibration configurations so as to eliminate the twist error constraints. The calibrated kinematic parameters and joint compliances are obtained eventually, and used to compensate the kinematic and compliance errors of the serial machining robot. Finally, to validate the effectiveness of the proposed unified error model, simulation analysis is performed using a 6-DOF serial machining robot, namely KUKA KR500. The comparisons among calibrated parameters show that the unified error model is more computationally efficient with optimal calibration configurations, rendering it suitable for the calibration of kinematic parameters and joint compliances in actual machining applications.
期刊:Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing(Volume 61, February 2020, 101855)
 鄂公网安备 42018502000562号
鄂公网安备 42018502000562号
